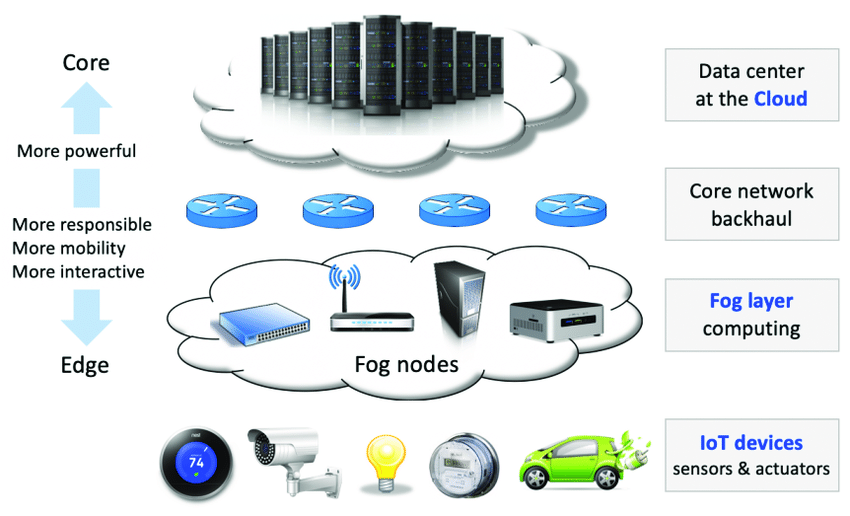
With rapidly increasing the Internet of things (IoT), the classic centralized cloud computing method has faced several challenges, such as high delay, low capacity, and network defects. Fog computing brings cloud waves closer to IoT devices to face these challenges. This fog provides processing and storage of IoT data locally on IoT devices instead of sending them to the cloud and provides faster response and better quality in contrast to the cloud. Therefore, it can be said that fog computations are the best choices for activating IoT to provide efficient and secure services to many users [1].
Various factors, such as service quality, price, justice, profit rate, load balance, etc. are influential in resource allocating. The resource allocation process is complex since both consumers and cloud providers are looking to make the most profit [2].
Fog computations are a promising architecture for low-cost, cost-effective data services for IoT-based network systems and rely on a set of low-power fog nodes adjacent to end-users.
Fog computing is a horizontal system-based architecture, providing the services and resources to the things supply chain for storing, computing, controlling, and networking at any place in the cloud. The fog computation layer introduced by Cisco expands the cloud space to the closest place where IoT data is generated and operated, these places are called as the fog nodes. Any device with processing and computing power, and in general computation, storage, and network communications, can be a fog node, such as industrial controllers, switches, routers, servers used in medical centers, hospitals, and video surveillance cameras, etc. In fog computing, data can be processed in smart devices instead of being sent to the cloud, and this is very interesting in the sense of IoT because it allows the real-time response to input data and is rendered with bandwidth [3]. Since fog can provide all the processed and stored data at a higher speed than cloud computing in the IoT for each node, the selection of the processing resources with maximum improvement is considered as an important issue in modeling.
An essential issue to achieve optimal and stable performance is allocating the fog nodes (FNs) with limited computational resources to all DSSs. Therefore, a common optimization framework is proposed in the present article for all DSSs, DSOs, and FNs to achieve optimal resource allocation schemes in a distribution method, in which a Stackelberg game has been used to analyze the resource allocation problem for DSSs and the pricing problem for DSOs. While the recognition of the expected amount of resources purchased by DSSs is possible by DSOs, checking for pairing between FNs and DSOs is performed by a many-to-many match game [4]. In conclusion, another layer of many-to-many matching is applied to the paired FNs in the same DSO, and solving the FNDSS pairing problem is performed by applying the DSS service. In the proposed method, the selection of fog processing layers will be made by a game-based model.
This algorithm performs the process of selecting the optimal resources for data processing in the fog layer, consideringboth energy and delay criteria at the same time. In this paper, a matching game framework, called Student Project Allocation (SPA), has been used for the purpose of distributing the solutions to the issue of the allocation of computational and radio resources, instead of the usually centralized optimization.
A productive SPA- (S, P) algorithm has been applied to solve the problem and the stable SPA results. In addition, the proposed user-oriented cooperation strategy (UOC) eliminates the external effects of instability, or, in other words, the independence between identical players. Finally, the efficiency of the system is measured after using the UOC strategy and comparing it with the previous study [5].
In this paper, the authors evaluate the impact of each of the cache parameters, CPU clock frequency performance, bandwidth, CPU cycle, aging, and IPC (Instruction per cycle/clock) to IoT-Fog users, to provide a model for allocating computational and radio resources in IoT computing. Some essential factors, including mandatory advantage, link quality, service delay, and other factors, have been considered, and a fog computing network is specifically designed to includea set of data service operators (DSOs). A set of fog nodes is controlled by every single DSO for transferring the needed data service to a set of data service subscribers (DSSs).
رایانش مه به عنوان یک رویکرد نوظهور برای تکامل بستر رایانش ابری و گسترش اینترنت اشیاء به لبه شبکه پیشنهاد شده است. در این نوع رایانش، ارائه دهندگان خدمات می توانند با تعیین وظایف خاص به کاربران ، سیگنال ها را کنترل کنند و وظایفی که نسبت به تأخیر بارگیری کاربران حساس هستند ، به گره های مه توزیع شده (FN) در لبه شبکه منتقل می شوند. در این مقاله ، نویسندگان موضوع تخصیص منابع رادیویی و محاسباتی مشترک با هدف بهینه سازی عملکرد سیستم و رضایت کاربر را مورد بررسی قرار خواهند داد. در این مقاله ، نویسندگان تأثیر هر یک از پارامترهای حافظه پنهان ، عملکرد فرکانس ساعت CPU ، پهنای باند ، چرخه CPU ، پیری و IPC (دستورالعمل در هر چرخه/ساعت) را برای کاربران IoT-Fog ارزیابی می کنند تا مدلی برای تخصیص محاسبات ارائه دهند. و منابع رادیویی در محاسبات اینترنت اشیا این الگوریتم فرایند انتخاب منابع بهینه برای پردازش داده ها در لایه مه را با در نظر گرفتن معیارهای انرژی و تأخیر به طور همزمان انجام می دهد. در این مقاله ، یک چارچوب بازی تطبیقی ، به نام تخصیص پروژه دانشجویی (SPA) ، به منظور توزیع راه حل های مربوط به موضوع تخصیص منابع محاسباتی و رادیویی ، به جای بهینه سازی معمولاً متمرکز ، مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. یک الگوریتم مولد SPA- (S، P) برای حل مشکل و نتایج SPA پایدار استفاده شده است. علاوه بر این ، استراتژی همکاری کاربر محور (UOC) اثرات خارجی بی ثباتی یا به عبارتی استقلال بین بازیگران یکسان را حذف کرد. نتایج نشان داد که چارچوب پیشنهادی در مقاله حاضر قادر به ارائه توزیع شده است و از نظر کاربران و سیستم به عملکرد مطلوب نزدیک است. بنابراین ، از رویکرد ترکیبی SPA- (S ، P) و UOC می توان برای تخصیص منابع محاسباتی و رادیویی مشترک در محاسبات مه برای محیط اینترنت اشیا استفاده کرد. همچنین ، از روش پیشنهادی این تحقیق می توان برای تخصیص رادیو مشترک استفاده کرد و منابع محاسباتی در دستگاههای با منابع محدود برنامه های حساس و محدودیت پهنای باند را در انواع محاسبات مه در محیط اینترنت اشیا به تأخیر انداخت.
برای مشاهده فایل کامل مقاله با عنوان
An Optimal Model to Improve the Allocation of Computational and Radio Resources in IoT Fog Computing
می توانید از اینجا بازدید کنید.
سفارش پروژه مشابه دارید؟ به این صفحه مراجعه کنید.
To view the full article file entitled:
An Optimal Model to Improve the Allocation of Computational and Radio Resources in IoT Fog Computing
You can visit here.
Do you have a similar project order? See this page.